How Much Power Does a 2.5 kW Air Conditioner Use?
When it comes to cooling your home or office space, air conditioners are essential appliances. However, it’s crucial to understand their power consumption to manage your energy usage effectively. In this article, we will explore the power requirements of a 2.5 kW air conditioner and help you make informed decisions about energy consumption and cost.
Understanding the Basics of Air Conditioner Power
Air conditioners are rated in terms of their cooling capacity, which is typically measured in kilowatts (kW). The cooling capacity indicates the amount of heat an air conditioner can remove from a room within a specific timeframe. In the case of a 2.5 kW air conditioner, it means that the unit can remove 2,500 watts of heat from the space.
However, it’s essential to differentiate between cooling capacity and power consumption. Cooling capacity is a measure of performance, while power consumption refers to the amount of electricity an air conditioner uses to achieve that cooling capacity.
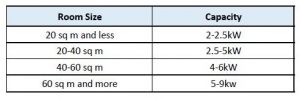
Calculating Power Consumption
To determine the power consumption of a 2.5 kW air conditioner, we need to consider its energy efficiency ratio (EER). The EER is a measure of how efficiently an air conditioner converts electrical input into cooling output.
Typically, the EER is calculated by dividing the cooling capacity (in watts) by the power consumption (in watts). For example, if a 2.5 kW air conditioner has an EER of 10, it means it consumes 250 watts of power to produce 2,500 watts of cooling.
Based on this information, we can conclude that a 2.5 kW air conditioner consumes 250 watts per kilowatt of cooling capacity. Consequently, when the air conditioner is operating at its full cooling capacity, it will consume 625 watts (2.5 kW x 250 watts/kW).
Factors Affecting Power Consumption
While the power consumption calculation mentioned above provides a general idea, it’s important to note that actual power usage can vary due to several factors. Here are some key elements that influence an air conditioner’s power consumption:
- Temperature Settings: Lowering the temperature on your air conditioner will increase its power consumption as the unit needs to work harder to achieve and maintain the desired temperature.
- Room Size and Insulation: Larger rooms or poorly insulated spaces may require the air conditioner to run for longer periods, resulting in higher power consumption.
- Climate Conditions: If you live in a hot and humid climate, your air conditioner may need to work harder and consume more power to provide effective cooling.
- Usage Patterns: The frequency and duration of air conditioner usage can significantly impact its power consumption. Constant usage or running the unit for extended periods will lead to higher energy consumption.
- Efficiency of the Air Conditioner: Different models and brands have varying energy efficiency levels. Investing in an energy-efficient air conditioner can help reduce power consumption.
Energy-Saving Tips for Air Conditioners
While air conditioners are essential for maintaining comfort during hot weather, there are several steps you can take to optimize their energy usage:
- Set the Temperature Wisely: Avoid setting the thermostat too low. Aim for a comfortable room temperature rather than excessively cold conditions. Each degree you raise the temperature can lead to significant energy savings.
- Utilize Programmable Thermostats: Invest in a programmable thermostat to set temperature schedules based on your needs. This allows you to reduce energy consumption when the space is unoccupied or during nighttime hours.
- Maintain Proper Insulation: Ensure that your home or office space is well-insulated to minimize heat transfer. Proper insulation can help retain cool air and reduce the workload on your air conditioner.
- Use Fans to Supplement Cooling: Use ceiling fans or portable fans to circulate cool air and create a breeze. This can help you feel more comfortable without solely relying on your air conditioner.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep your air conditioner clean and well-maintained. Clean or replace air filters regularly, and schedule professional maintenance to optimize its performance and efficiency.
- Avoid Heat Sources: Minimize the use of heat-generating appliances during the hottest parts of the day. Heat-producing devices, such as ovens, stoves, and dryers, can make your air conditioner work harder.
Conclusion
When considering the power consumption of a 2.5 kW air conditioner, it’s important to remember that the cooling capacity and power usage are not the same. By understanding the relationship between cooling capacity, energy efficiency ratio, and power consumption, you can estimate the electricity requirements of your air conditioner.

Factors such as temperature settings, room size, climate conditions, usage patterns, and the efficiency of the air conditioner can influence its power consumption. Implementing energy-saving practices, such as optimizing temperature settings, using programmable thermostats, maintaining insulation, and utilizing fans, can help reduce energy usage without compromising comfort. https://jbqualityairconditioning.com.au/evaporative-air-conditioner-servicing-northern-suburbs/
By making informed decisions and implementing energy-efficient practices, you can not only manage your power consumption but also contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly environment.


